The next generation of wireless technology is here. 5G will enhance connectivity across all platforms, providing more efficient, faster and better signal strength which opens doors for new possibilities across cellular networks. It is predicted that by 2024 more than 1.5 billion devices will be connected to 5G.1 So how will 5G enhance your cellular connectivity?
Differentiating Between 4G and 5G
5G will be a strong enabler in the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), given the speed and versatility it will bring to networks. 5G has a range of benefits when compared to 4G, based on its use of the 30 GHz to 300 GHz spectrum:
- Higher speeds: 5G peak speeds, at up to10 Gigabits/s, will potentially be ten times the speed of 4G. 2
- Lower Latency: 5G offers latency below 1ms, compared to a typical 4G performance of 10-50ms. 2
- Greater capacity: 5G networks will have capacity for a larger number of connected devices, by some estimates as much as one million devices per square kilometer3
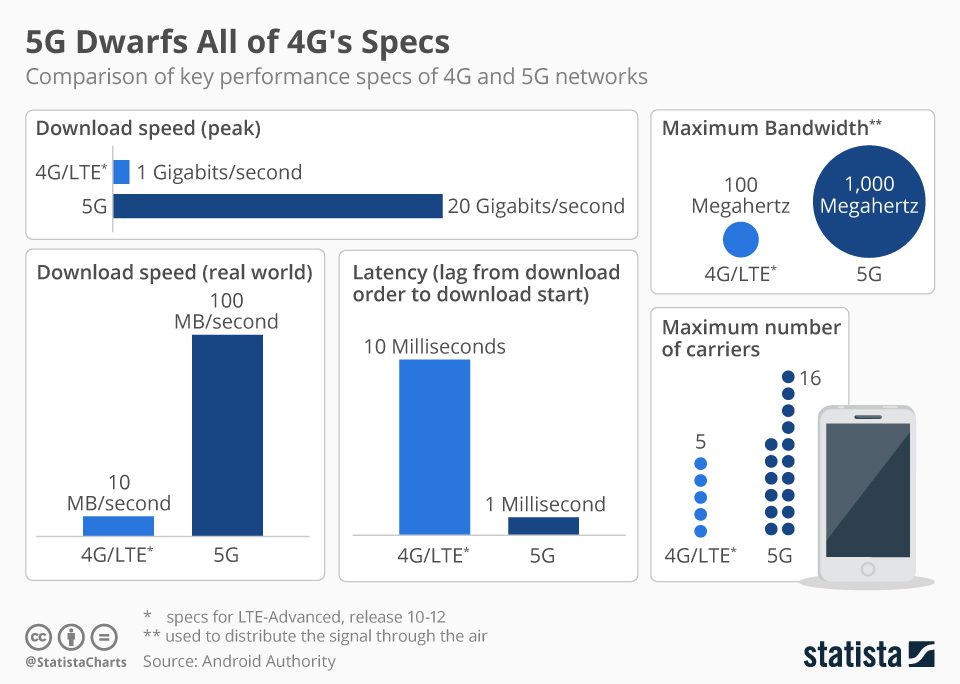
Ref: Statista
5G is gradually being rolled out, so later iterations are expected to have even stronger capabilities.
It’s important to note that 5G, unlike previous iterations, is not expected to replace 4G. Many applications, such as standard mobile phone calls and low-data transactions, will still be carried on a 4G network, with 5G being applied primarily to large-compute and low-latency uses.
Given the higher frequency spectrum, 5G also requires a higher density of towers to cover a given area, meaning that rollout of 5G will initially be limited to metropolitan areas. It is also impacted more severely by physical barriers such as walls, trees, and even bad weather.
5G, IoT and the Edge
Compute locations are moving increasingly to the edge, driven by the growth of IoT and the desire to process and prioritize data closer to the collection point. Faster connections associated with 5G will support that migration as enterprises distribute their network power between Data Centers, Cloud Computing and the Edge.
The low latency and high speed of 5G particularly suit applications such as consumer VR/AR, AI, and autonomous vehicles, with high data density and rapid response requirements, enabling faster adoption of these technologies.
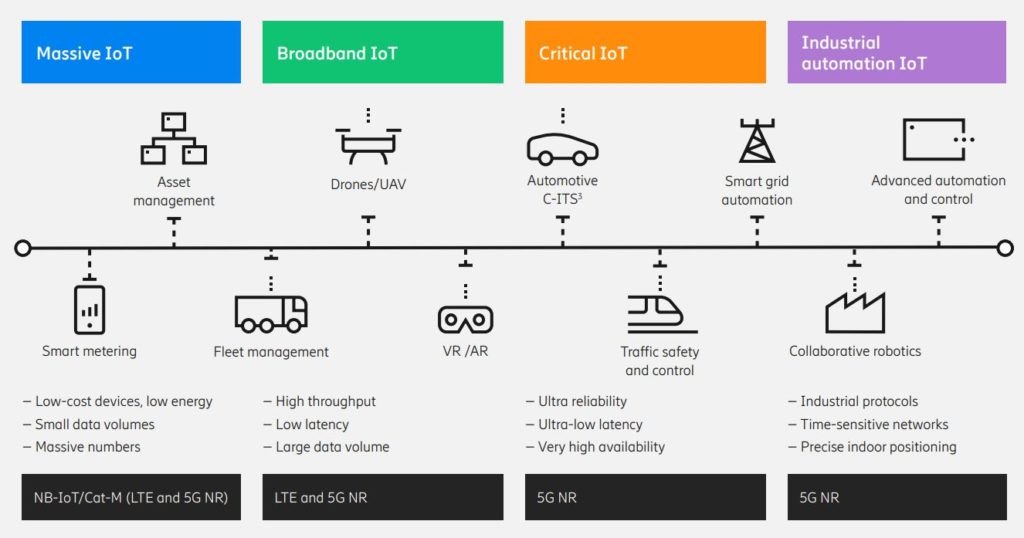
Cellular IoT use case segments
Credit: Ericsson Mobility Report, June 2019
5G and Out-of-Band
Users expect the same level of uptime and response from their network, regardless of where that compute is located. But the reality of edge locations is that the type of system redundancy and staffing that is typical at data centers are not feasible at each location. Reliable, always-on access to the network devices, via out-of-band management, is a critical component of that network resilience.
As levels of automation continue to increase, enterprises will also have to extend the reach of their management and monitoring tools. Opengear solutions anticipate the current and future network needs of 5G.
Opengear smart solutions provide engineers at the Network Operations Center (NOC) with the ability to reach devices located at the edge. Lighthouse ensures access and visibility remotely, during critical failures while Smart Out-of-Band provides advanced troubleshooting to remediate issues that may arise at the network’s edge. The Network Resilience Platform provides additional functionality to streamline repetitive workflows such as secure provisioning and event management.
Deciding When to Adopt
Each organization has a core IT infrastructure and line of business applications. Constantly improving technologies provide an opportunity to help them operate more efficiently. Once the right technologies have been identified, enterprises must identify the right moment to get on board to ensure meaningful results.
For 5G specifically, determining the right time to act requires understanding the most immediate use cases for it within the enterprise. The first is fixed internet connectivity. Instead of using cable, satellite or copper wires/ADSL, edge locations could potentially use 5G to get fixed internet connectivity. Because this eliminates the need for burdensome physical cables and wires, 5G may provide an easier method for deployment.
For many enterprises, it is too early to fully embrace 5G. Unless there are already specific applications that are limited by speed/latency of existing connectivity technologies, the value of deploying it will not yet be realized. Instead, the focus, for now, should be on understanding the technology at a high level and identifying the use cases that are likely to benefit the business most so that they can be prioritized when 5G becomes readily available.
2. https://www.digitaltrends.com/mobile/5g-vs-4g/
3. https://www.androidauthority.com/what-is-5g-explained-944868/
